At The Brain and Spine Centre, we specialize in the diagnosis and surgical treatment of neurological and spinal disorders. Dr. Muhammad Aqeel Natt, a leading neurosurgeon in Lahore, provides advanced, safe, and compassionate care for patients.

Stereotactic Neurosurgery
Stereotactic neurosurgery is a precision-guided surgical approach that uses advanced three-dimensional imaging and computer-assisted navigation to accurately target specific intracranial lesions with millimeter precision. At The Brain and Spine Centre, Dr. Muhammad Aqeel Natt offers state-of-the-art stereotactic neurosurgery at Farooq Hospital, West Wood Branch, Lahore, using both frame-based and frameless systems to safely access and treat deep-seated, eloquent, or complex brain lesions with minimal trauma.
Our goal is simple: achieve precise diagnosis or treatment safely, protect neurological function, and minimize surgical trauma.
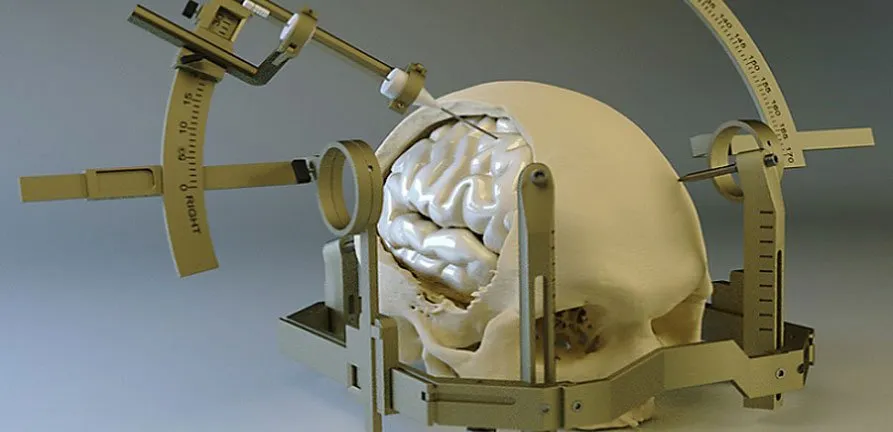
What Is Stereotactic Neurosurgery?
Stereotactic neurosurgery is a minimally invasive surgical technique that localizes and accesses brain lesions using a three-dimensional coordinate system established by preoperative MRI or CT imaging combined with real-time intraoperative navigation. The term “stereotactic” refers to this precise 3D coordinate mapping system, which allows surgeons to target lesions with millimeter accuracy without requiring large surgical exposure. Stereotactic techniques revolutionize access to deep, eloquent, multifocal, or previously inaccessible brain regions.
Two main technological approaches:
Frame-based stereotaxy:
- Rigid stereotactic frame is affixed to the skull using four pins under local anesthesia.
- Imaging with fiducials visible is performed while frame in place, enabling precise coordinate calculation.
- Offers superior accuracy (1.85±1.28 degree trajectory deviation) and is considered the gold standard.
- Can be performed under local anesthesia with sedation.
Frameless stereotaxy (neuronavigation):
- Uses surface fiducials (markers) on the scalp or head for registration without a rigid frame.
- Intraoperative tracking system (electromagnetic, optical, or acoustic) continuously monitors probe position relative to preoperative images.
- Greater patient comfort and flexibility; imaging can be obtained days prior to surgery.
- Comparable accuracy to frame-based (2.63±1.58 degree trajectory deviation) with slightly more angular error.
- Usually requires general anesthesia.
- Better suited for midline and multifocal lesions.
Indications for Stereotactic Neurosurgery
Preoperative planning for stereotactic procedures:
- High-resolution MRI (1.5–3.0 Tesla) with thin-cut sequences (1–2 mm) and fiducials for frame-based studies, or dedicated neuronavigation sequences for frameless.
- CT imaging with frames in place (frame-based) or MR-compatible markers for registration.
- Advanced sequences such as DTI, perfusion, and functional MRI to identify eloquent areas and plan safe trajectories.
- Vascular imaging (MR or CT angiography) to avoid major vessels.
Diagnosis
Preoperative planning for stereotactic procedures:
- High-resolution MRI (1.5–3.0 Tesla) with thin-cut sequences (1–2 mm) and fiducials for frame-based studies, or dedicated neuronavigation sequences for frameless.
- CT imaging with frames in place (frame-based) or MR-compatible markers for registration.
- Advanced sequences such as DTI, perfusion, and functional MRI to identify eloquent areas and plan safe trajectories.
- Vascular imaging (MR or CT angiography) to avoid major vessels.
The Procedure
Stereotactic neurosurgery ensures high accuracy and minimal brain trauma.
Frame-based approach:
- Stereotactic frame applied to skull under local anesthesia with four skull pins.
- High-resolution imaging performed with frame in place; fiducials visible on all images.
- Surgeon calculates target coordinates and trajectory using planning software.
- In operating room, target location and safe path are verified.
- Small burr hole created at calculated entry point using frame guidance.
- Biopsy needle, aspirator, or other instruments advanced along predetermined trajectory.
- Intraoperative frozen-section analysis confirms diagnostic adequacy; therapeutic procedures completed per plan.
Frameless approach:
- Fiducials placed on scalp under local anesthesia or after anesthesia induction.
- Preoperative MRI/CT obtained and loaded into neuronavigation workstation.
- Registration process aligns patient anatomy with preoperative images using fiducials.
- Intraoperative tracking system continuously displays probe position on preoperative images in real-time.
- Surgeon maintains image-guidance throughout procedure, adjusting trajectory as needed.
- Small burr hole and minimally invasive access achieved with precise targeting.
Recovery & Aftercare
Recovery is remarkably rapid due to minimal surgical trauma.
- Hospital stay: Often same-day or 1–2 days depending on procedure type.
- Immediate postoperative imaging: CT or MRI performed to exclude hemorrhage or complications.
- Activity resumption: Most patients return to normal activities within 1–2 days.
- Complications: Minimal with modern techniques; diagnostic yield high (89–98%), diagnostic accuracy comparable between frame-based and frameless.
- Pathology results: Preliminary frozen-section results available during surgery; final pathology in 5–7 days.
Results You Can Expect
Diagnostic accuracy:
- Frame-based and frameless stereotactic biopsies achieve diagnostic yield of 89–98% and comparable diagnostic accuracy.
- No statistically significant difference in target distance or trajectory length between techniques.
- Both approaches provide safe, accurate tissue diagnosis with minimal morbidity.
Procedural safety:
- Procedure-related morbidity rates 1–13.3%; serious adverse events rare.
- Infection rates <7%, seizure rates ~10%.
- Mortality essentially zero for diagnostic procedures.
Therapeutic outcomes:
- Minimally invasive access enables treatment of previously surgically inaccessible lesions.
- Reduced surgical trauma compared to open resection translates to faster recovery, lower morbidity, and preserved neurological function.
- DBS and ablative procedures achieve excellent functional outcomes with precise targeting.
Why Choose The Brain and Spine Centre
Led by Dr. Muhammad Aqeel Natt, specialist neurosurgeon with extensive experience in both frame-based and frameless stereotactic neurosurgery and comprehensive expertise in minimally invasive access to complex brain lesions. Access to high-resolution preoperative imaging (3.0 Tesla MRI with advanced sequences) and modern neuronavigation systems ensuring superior targeting accuracy. Expertise in both diagnostic (biopsy, aspiration) and therapeutic (resection, DBS, ablation) stereotactic procedures, tailored to patient pathology. Rapid intraoperative frozen-section pathology and expert neuropathology consultation enabling immediate diagnostic results and optimal treatment decisions. Safety-focused approach minimizing trauma and maximizing preservation of neurological function through precision-guided, minimally invasive access.
Cost of Stereotactic Neurosurgery
Costs vary with procedure type (diagnostic vs. therapeutic), frame-based vs. frameless technique, imaging requirements, hospital stay, intraoperative frozen-section analysis, and pathology testing complexity. Personalized cost estimates provided after consultation and imaging review.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can I know Dr. Muhammad Aqeel Natt’s credentials?
What types of brain tumours do you treat?
Is the surgery safe?
Do I need long-term follow-up after surgery?
Are you having health problems? Contact us today!
Address Business
Contact With Us
Call Us 24/7: 0318 4065914
Working Time
Sunday: 8.30am - 19.30pm

