At The Brain and Spine Centre, we specialize in the diagnosis and surgical treatment of neurological and spinal disorders. Dr. Muhammad Aqeel Natt, a leading neurosurgeon in Lahore, provides advanced, safe, and compassionate care for patients.

Awake Craniotomy
Awake craniotomy is an advanced neurosurgical technique that enables maximal tumor removal while preserving critical brain functions. At The Brain and Spine Centre, Dr. Muhammad Aqeel Natt provides specialized awake craniotomy services at Farooq Hospital, West Wood Branch, Lahore, combining precision surgery with real-time neurological monitoring.
Our goal is simple: remove tumor safely, preserve brain function, and guide recovery for optimal quality of life.
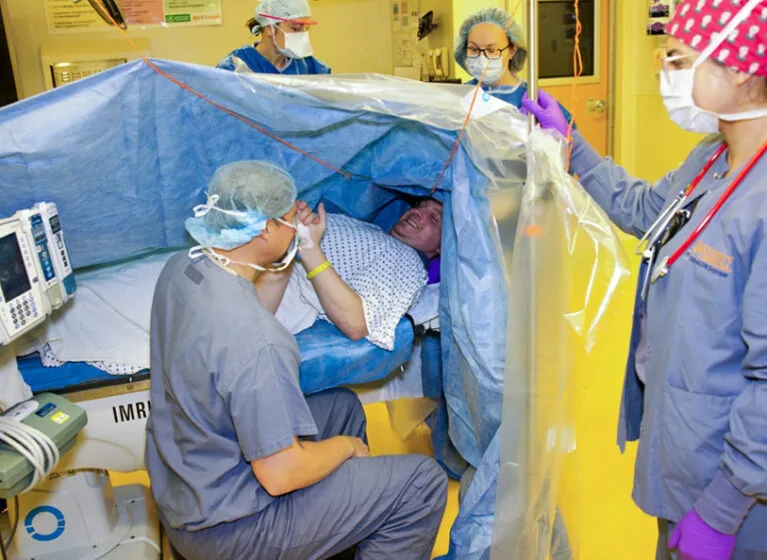
What Is an Awake Craniotomy?
Awake craniotomy is a neurosurgical procedure performed while the patient is conscious (awake) for at least part of the surgery. The skull is opened under general anesthesia, but once the brain is exposed, the patient is gently awakened so the surgical team can perform real-time brain mapping and monitor neurological function while removing the tumor. This approach allows surgeons to pinpoint critical brain areas controlling speech, movement, sensation, and cognition, minimizing the risk of permanent neurological damage.
The procedure is not entirely “awake” as the term suggests. Patients sleep during initial craniotomy and closure phases with intense surgical stimulation, remaining sedated and comfortable, then are awakened for the critical tumor resection and brain mapping phase.
Indications for Awake Craniotomy
Ideal candidates for awake craniotomy include patients with:
Tumors located adjacent to or within eloquent brain areas controlling speech, movement, sensation, vision, or cognitive functions, gliomas (high-grade and low-grade) in supratentorial locations, cortical and subcortical lesions near functional brain areas, epileptic foci requiring surgical removal, and patients with good cognitive function, adequate communication ability, and willingness to cooperate during the procedure.
Patient selection requires:
Age typically 14 years or older with ability to cooperate, mental status clear enough to participate in testing and communicate concerns, fluency in a language understood by the operating team, and psychological readiness and motivation for the procedure.
Symptoms Addressed
Awake craniotomy is indicated for treating:
Brain tumors causing neurological deficits including weakness, speech problems, vision loss, or cognitive changes, epilepsy with seizure foci localized to eloquent brain areas, and other lesions causing neurological symptoms located near critical brain functions.
Diagnosis
Pre-operative imaging and testing establish baseline function:
Advanced imaging:
High-field MRI (3.0 Tesla) with functional MRI (fMRI) to identify eloquent areas controlling motor, language, and cognitive functions. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) maps white matter tracts crucial for neurological function.
Neuronavigation planning: Three-dimensional image guidance systems are used to plan the safest surgical approach and trajectory.
Baseline neuropsychological testing: Cognitive, language, and motor assessments establish baseline function before surgery.
Treatment: The Awake Craniotomy Procedure
Anesthetic technique:
Patients receive light-to-moderate sedation with propofol and remifentanil infusions, allowing spontaneous breathing and arousability without airway manipulation. No general anesthesia during the mapping phase to ensure patient cooperation.
Surgical phases:
Phase 1 (Asleep): Induction of general anesthesia, positioning, rigid head fixation with pins, and craniotomy (opening skull) under general anesthesia.
Phase 2 (Awake): Patient is awakened through careful titration of sedation. Brain cortex is exposed for intraoperative brain mapping. Electrical stimulation mapping is performed to identify motor, language, sensory, and cognitive areas. Patient performs tasks such as speaking, moving limbs, counting, reading, or cognitive exercises while surgeons stimulate different brain regions.
Phase 3 (Resection): Tumor is carefully resected while monitoring for neurological changes. Surgeon adjusts surgical trajectory and extent based on real-time patient feedback and brain mapping results.
Phase 4 (Closure): Once tumor resection is complete, patient is re-sedated for hemostasis, dura closure, bone flap replacement, and scalp closure.
Mapping techniques:
Direct cortical/subcortical electrical stimulation to identify functional areas, electrocorticography (ECoG) to detect brain electrical activity, motor and language evoked potentials to monitor pathway integrity, and real-time intraoperative neuromonitoring throughout.
Recovery & Aftercare
Approximately 1-2 hours for full recovery from anesthesia effects. Patients are monitored in intensive care unit for blood pressure control, intracranial pressure management, pain control, temperature regulation, and neurological assessments.
Hospital stay:
Average 3-5 days compared to 9+ days for traditional general anesthesia approaches. Some patients discharged within 24-48 hours depending on complications.
Common post-operative experiences:
Temporary neurological deficits such as speech difficulties, weakness, or balance problems that typically resolve within 1-3 months. Headaches described as pulsating or pounding, common and can persist several months. Swelling and bruising of the face and incision site. High blood pressure, nausea, vomiting managed with medications.
Recovery timeline:
Bone flap heals within 2-3 months and partially fuses back into skull. Full neurological recovery may take several months. Most patients recover almost completely within 1-3 months. Some patients show improvement in cognitive and emotional function up to 6 months post-surgery.
Rehabilitation:
Physical, occupational, and speech therapy address any persisting deficits. Cognitive rehabilitation if needed. Gradual return to activities over weeks to months.
Neuropsychological monitoring:
Follow-up cognitive testing assesses recovery trajectory. Emotional and psychological support. Return to work typically several weeks after surgery.
Results You Can Expect
Maximal tumor resection: Awake craniotomy enables greater tumor removal compared to general anesthesia approaches while preserving function. Studies show significantly higher extent of resection achieved with awake techniques.
Improved functional preservation: Only 7% of patients experience long-term neurological deficits with awake craniotomy compared to 23% with general anesthesia. Approximately 90% of temporary neurological deficits resolve in the post-operative period.
Neurological outcomes: Most patients experience minimal cognitive or emotional decline, with many recovering within 3-6 months. Some patients even show improvements in executive function, memory, language, and emotion recognition. Long-term neurological deficits are significantly lower in awake craniotomy (9 patients) compared to general anesthesia (18 patients).
Survival and tumor control: Reported survival rates exceed 90% with awake mapping techniques. Optimal tumor resection leads to favorable oncological outcomes.
Quality of life: No significant difference in quality-of-life scores between awake and general anesthesia groups, but awake craniotomy achieves better outcomes with less extensive resection in general anesthesia group. Most patients report overall satisfaction with the procedure.
Hospital efficiency: Average reduction of 4-8 days in hospital stay compared to general anesthesia. Faster discharge enables quicker return to daily activities.
Why Choose The Brain and Spine Centre
Led by Dr. Muhammad Aqeel Natt, specialist neurosurgeon with extensive expertise in awake craniotomy, intraoperative brain mapping, and maximally safe tumor resection. Access to advanced imaging including 3.0 Tesla MRI with fMRI and DTI for precise functional mapping and surgical planning. State-of-the-art intraoperative neuromonitoring including electrical stimulation mapping, ECoG, motor/language evoked potentials, and real-time navigation systems. Experienced multidisciplinary team including anesthesiologists skilled in awake anesthesia techniques, neurophysiologists for real-time monitoring, and rehabilitation specialists. Commitment to patient comfort and psychological support throughout the procedure. Convenient location at Farooq Hospital, West Wood Branch, Lahore with comprehensive neurosurgical capabilities.
Cost of Awake Craniotomy
Costs vary with tumor location and complexity, extent of brain mapping required, duration of surgery, imaging studies, intraoperative monitoring technology, hospitalization duration, and rehabilitation services. Personalized estimates provided after consultation and imaging evaluation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can I know Dr. Muhammad Aqeel Natt’s credentials?
What types of brain tumours do you treat?
Is the surgery safe?
Do I need long-term follow-up after surgery?
Are you having health problems? Contact us today!
Address Business
Contact With Us
Call Us 24/7: 0318 4065914
Working Time
Sunday: 8.30am - 19.30pm

