At The Brain and Spine Centre, we specialize in the diagnosis and surgical treatment of neurological and spinal disorders. Dr. Muhammad Aqeel Natt, a leading neurosurgeon in Lahore, provides advanced, safe, and compassionate care for patients.

Brain Abscess
Brain abscess is a serious, potentially life-threatening infection in which a pocket of pus forms within brain tissue, causing swelling and pressure on surrounding structures. At The Brain and Spine Centre, Dr. Muhammad Aqeel Natt provides urgent neurosurgical and medical management of brain abscesses at Farooq Hospital, West Wood Branch, Lahore, combining advanced imaging, targeted antibiotics, and minimally invasive drainage techniques.
Our goal is simple: control the infection, relieve pressure on the brain, and prevent neurological damage or recurrence.
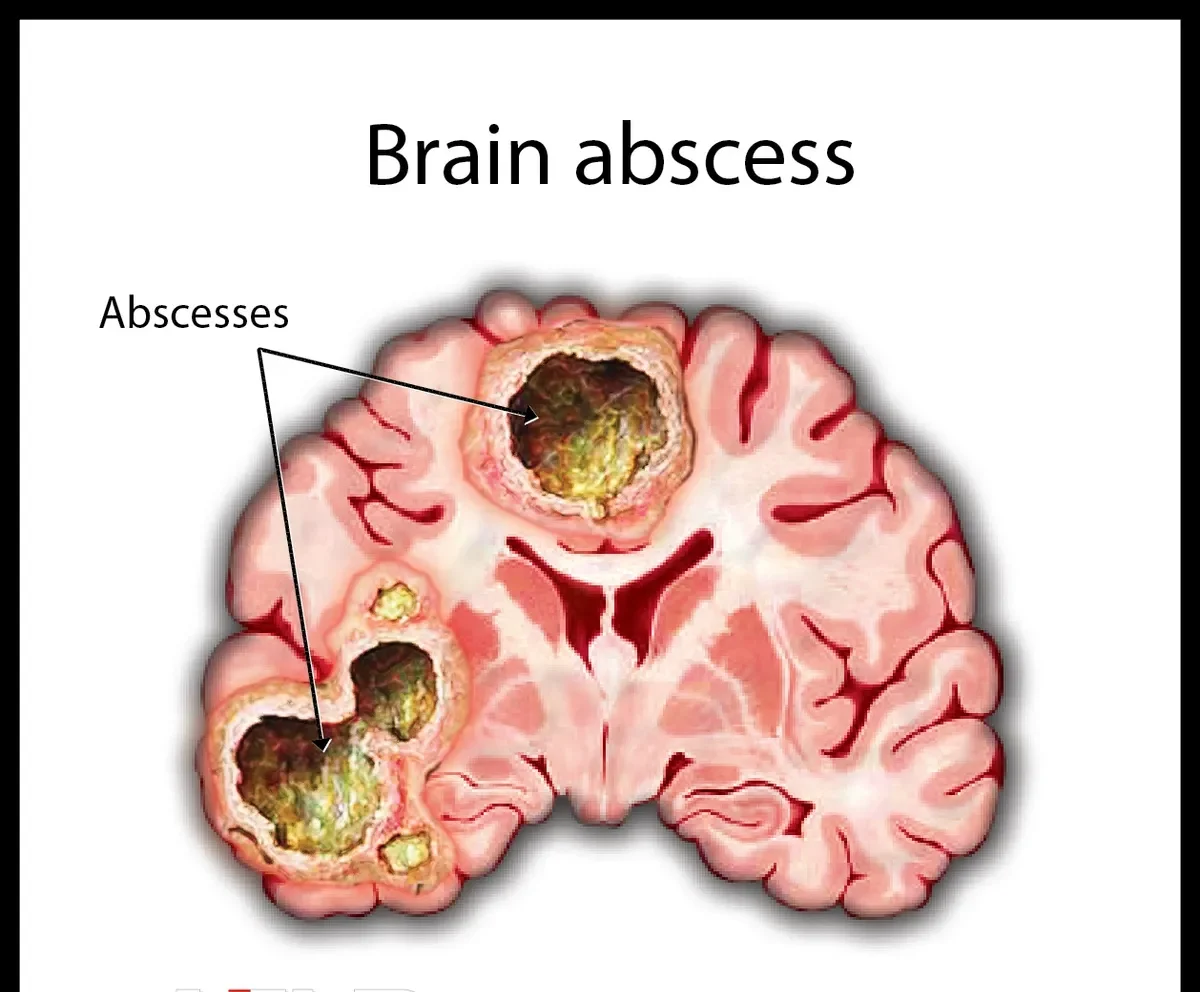
What Is a Brain Abscess?
A brain abscess is a localized collection of pus (infected brain tissue, organisms, white blood cells, and debris) surrounded by a vascular capsule within the brain parenchyma. It develops when bacteria, fungi, or (rarely) parasites reach the brain either from nearby infected sites, through the bloodstream, or after trauma/neurosurgery.
Common sources:
Contiguous infections: chronic otitis media, mastoiditis, sinusitis, dental infections.
Hematogenous spread: lung abscess, pneumonia, bronchiectasis, endocarditis, abdominal or pelvic sepsis.
Trauma/neurosurgery: open skull fractures, penetrating injuries, postoperative infections.
Immunocompromised states (HIV, chemotherapy, transplant, uncontrolled diabetes) increase risk.
Symptoms of Brain Abscess
Symptoms reflect infection, local tissue destruction, and mass effect.
Common features:
Headache (most frequent symptom), often localized and progressively worsening; sudden severe worsening may suggest rupture.
Fever, chills, malaise (classical triad of headache, fever, and focal neurological deficit occurs in fewer than half of patients).
Focal neurological deficits: weakness or paralysis on one side, speech disturbance, visual field deficits, ataxia depending on abscess location.
Altered mental status: confusion, drowsiness, irritability, poor concentration, slow mentation, up to coma in severe cases.
Seizures in up to 25–35% of patients.
Signs of raised intracranial pressure: nausea, vomiting, papilloedema, reduced consciousness.
Neck stiffness and photophobia may occur, especially if abscess ruptures into the ventricles or subarachnoid space.
Diagnosis
Rapid imaging and microbiological evaluation are critical.
Imaging:
Contrast-enhanced MRI is the most sensitive and specific modality; typical ring‑enhancing lesion with central restricted diffusion (pus) on DWI helps distinguish abscess from necrotic tumour.
Contrast-enhanced CT is widely available and essential in emergency settings; shows hypodense lesion with ring enhancement and surrounding oedema but cannot reliably differentiate tumour vs abscess without MRI and clinical context.
Multiple lesions are not uncommon and may reflect hematogenous spread.
Microbiology:
Blood cultures, and if safe, CT‑guided stereotactic aspiration or surgical drainage to obtain pus for Gram stain, culture, and sensitivity.
Differential diagnosis includes high-grade glioma, metastasis, and infarction; MRI with DWI, MR spectroscopy, and, when needed, biopsy help differentiate.
Treatment Options
Management combines high-dose, prolonged intravenous antibiotics with surgical drainage when indicated.
Antibiotic therapy:
Empiric broad-spectrum IV antibiotics started immediately, tailored once cultures identify organisms.
Typical duration: 4–8 weeks of IV therapy, sometimes followed by oral antibiotics depending on clinical and radiological response.
Surgical management:
Indications for surgery: abscess ≥2–2.5 cm, significant mass effect or raised intracranial pressure, uncertain diagnosis, failure to improve on antibiotics, multiloculated or atypical lesions, or accessible superficial capsules.
Stereotactic or CT‑guided aspiration: burr‑hole or twist‑drill craniostomy with image‑guided aspiration of pus; allows decompression and culture with minimal invasiveness; often preferred for deep or eloquent-area abscesses.
Craniotomy and capsule excision: considered for large, superficial, firm, multiloculated abscesses or when repeated aspirations fail; some series show shorter hospital stay and antibiotic duration but at cost of greater invasiveness.
Management of complications: control of seizures, management of raised intracranial pressure (osmotherapy, steroids in selected cases, CSF diversion if hydrocephalus), treatment of the primary infection source.
The Procedure
At The Brain and Spine Centre:
Initial assessment: rapid CT/MRI to localise abscess, evaluate number and size, and screen for mass effect or hydrocephalus.
Decision-making: neurosurgical and infectious diseases teams decide on antibiotics alone vs image‑guided aspiration vs craniotomy based on lesion characteristics and clinical status.
Surgical technique: stereotactic burr‑hole aspiration or open craniotomy and capsule excision in selected cases, with intraoperative collection of pus for microbiology and histology.
Postoperative care: ICU or high-dependency monitoring, serial neurological exams, and repeat imaging to assess abscess size and response to therapy.
Recovery & Aftercare
Recovery depends on initial neurological status, abscess size/location, and speed of treatment.
Clinical improvement in headache, fever, and focal deficits expected over days to weeks; radiological resolution lags behind and may take weeks to months.
Serial CT/MRI scans guide duration of antibiotics and detect residual or recurrent abscess.
Long-term follow-up for seizure control, rehabilitation for residual deficits, and monitoring of the primary infection source (e.g., sinus, ear, lung, heart).
Results You Can Expect
With modern imaging, neurosurgery, and antibiotics:
Overall mortality has fallen significantly and is now often in the range of 10–20% or less in specialised centres, depending on series and patient comorbidities.
Many survivors regain good functional status, especially when treated early, with single, superficial abscesses and minimal preoperative deficits.
Poor prognostic factors include delayed diagnosis, multiple abscesses, deep locations (e.g., brainstem), severe immunosuppression, coma at presentation, and intraventricular rupture.
Why Choose The Brain and Spine Centre
Led by Dr. Muhammad Aqeel Natt, with expertise in stereotactic aspiration, craniotomy, and multidisciplinary neuro‑infectious disease management. Access to high‑quality MRI, CT, and stereotactic systems for accurate localisation and minimally invasive drainage. Close collaboration with infectious diseases, ENT, pulmonology, and cardiology to identify and eradicate primary infection sources and tailor antibiotic regimens. Structured follow‑up and rehabilitation to manage neurological sequelae and reduce recurrence risk.
Cost of Brain Abscess Treatment
Costs depend on imaging, length of ICU and hospital stay, choice of surgical approach (aspiration vs excision), antibiotic duration, and rehabilitation needs. Personalised cost estimates are provided after clinical and imaging evaluation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can I know Dr. Muhammad Aqeel Natt’s credentials?
What types of brain tumours do you treat?
Is the surgery safe?
Do I need long-term follow-up after surgery?
Are you having health problems? Contact us today!
Address Business
Contact With Us
Call Us 24/7: 0318 4065914
Working Time
Sunday: 8.30am - 19.30pm

