At The Brain and Spine Centre, we specialize in the diagnosis and surgical treatment of neurological and spinal disorders. Dr. Muhammad Aqeel Natt, a leading neurosurgeon in Lahore, provides advanced, safe, and compassionate care for patients.

Pituitary Tumors / Craniopharyngiomas
Pituitary tumors and craniopharyngiomas require prompt, expert diagnosis and individualized treatment to manage hormonal imbalances and preserve neurological function. At The Brain and Spine Centre, Dr. Muhammad Aqeel Natt provides specialized care for these complex tumors at Farooq Hospital, West Wood Branch, Lahore, combining advanced neurosurgical expertise with compassionate support.
Our goal is simple: remove tumor safely, restore hormonal balance, and guide recovery for the best possible quality of life.
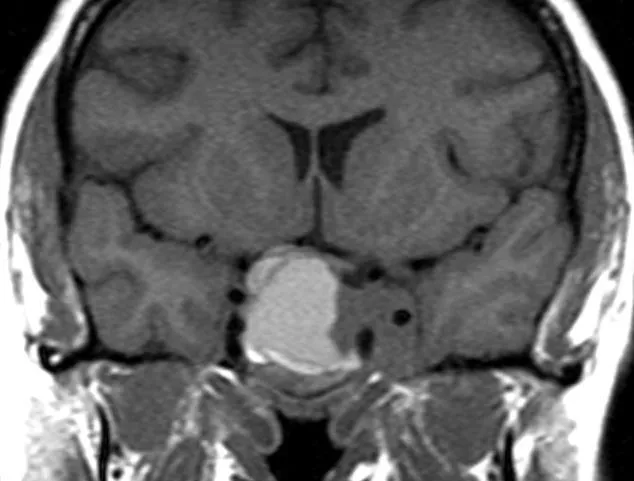
What Are Pituitary Tumors and Craniopharyngiomas?
Pituitary tumors (pituitary adenomas) are benign growths on the pituitary gland, a small gland at the base of the brain responsible for producing hormones that regulate growth, metabolism, reproduction, and stress response. They are the third most common intracranial tumor. Pituitary adenomas are classified by size as microadenomas (less than 1 cm) or macroadenomas (1 cm or larger), and by hormone production as functioning (producing excess hormones) or non-functioning (not producing hormones).
Craniopharyngiomas are rare, non-cancerous brain tumors that grow near the base of the brain, just above the pituitary gland. They can affect children and adults and, although benign, can cause significant symptoms by compressing the pituitary gland, optic nerves, and hypothalamus. In adults, less than 1% of brain tumors are craniopharyngiomas.
Symptoms of Pituitary Tumors and Craniopharyngiomas
Symptoms depend on tumor size, location, and hormone production.
Common symptoms of pituitary tumors include:
Headaches, vision problems including blurred vision or loss of peripheral vision, fatigue, unexplained weight gain or loss, menstrual irregularities, decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, nausea and vomiting, and symptoms specific to hormone-secreting tumors such as acromegaly (enlarged hands, feet, facial features), Cushing’s disease (weight gain, rounded face, purple striae), or hyperthyroidism (palpitations, weight loss, tremors).
Common symptoms of craniopharyngiomas include:
Headaches, especially persistent morning headaches, vision problems including blurry vision, double vision, or tunnel vision, hormonal changes causing growth failure, delayed puberty in children, or diabetes insipidus (excessive thirst and urination), cognitive changes including memory troubles, mood swings, or personality changes, nausea and vomiting, sleepiness or abnormal fatigue, loss of balance or trouble walking, and weight gain.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis begins with neurological examination and hormone level assessment through blood tests. Imaging studies confirm diagnosis and guide treatment planning.
Imaging options include:
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) with and without contrast is the gold standard for diagnosing both pituitary tumors and craniopharyngiomas. MRI provides highly detailed images of soft tissue, tumor characteristics, and relationship to surrounding structures.
Computerized Tomography (CT) scan can show calcifications commonly seen in craniopharyngiomas and is useful when MRI is unavailable or contraindicated.
Hormone testing through blood work measures levels of pituitary hormones, cortisol, growth hormone, prolactin, thyroid hormones, and sex hormones to identify hormonal imbalances caused by the tumor.
Eye examination evaluates vision changes and detects pressure on optic nerves.
Treatment Options
Surgery: Transsphenoidal surgery is the most common and preferred approach for pituitary tumors, accessing the tumor through the nasal passages without opening the skull. This minimally invasive approach leaves no visible scar, minimizes complications, and enables faster recovery. For craniopharyngiomas, surgery aims to remove all or as much tumor as safely possible. Complete surgical removal offers the best outcomes.
Medication therapy: Drug therapy is the first-line treatment for prolactin-secreting tumors (prolactinomas), which often respond well to medications that block prolactin production. Medications may also be used for growth hormone-secreting and ACTH-secreting tumors to control hormone levels.
Radiation therapy: Radiation is used for residual tumors after surgery, recurrent tumors, or when surgery is not possible. Stereotactic radiosurgery delivers focused radiation in one or few sessions with minimal damage to surrounding tissue. Conventional radiation therapy is delivered in smaller doses over several weeks.
Hormone replacement therapy: Following surgery or radiation, many patients require lifelong hormone replacement for deficiencies in thyroid hormone, cortisol, sex hormones, or growth hormone.
The Procedure
Our process safeguards safety, hormonal balance, and optimal outcomes:
Consultation: Comprehensive evaluation including neurological examination, hormone level assessment, and imaging review to determine tumor type, size, and treatment approach.
Imaging: Advanced MRI with or without contrast, CT scans, and hormone testing to characterize tumor and assess pituitary function.
Surgery (if indicated): Transsphenoidal approach through nasal passages for pituitary tumors, or craniotomy if necessary for larger tumors or craniopharyngiomas. Surgery performed with intraoperative monitoring to protect vision and neurological functions.
Hormone evaluation: Endocrinologist evaluates hormone levels following surgery to assess pituitary function and determine need for hormone replacement.
Recovery: Inpatient monitoring for 2-3 days in the hospital, followed by 4-6 weeks of at-home recovery.
Recovery & Aftercare
Most patients spend 2-3 days in the hospital after transsphenoidal surgery and approximately 4-6 weeks recovering at home. Patients may experience nasal discharge, congestion, and headaches initially, which typically resolve with time. Blood hormone level testing is performed within days to weeks after surgery to assess treatment success and pituitary function.
Hormone replacement therapy is often necessary and may be lifelong, including thyroid hormone, adrenal steroids, testosterone, estrogen, or growth hormone depending on deficiencies. Regular medication management and dosage adjustments are common as hormone levels stabilize. Physical and emotional well-being support is integral to holistic recovery. Long-term follow-up with regular MRI scans and hormone level checks monitors for recurrence and manages hormonal imbalances.
Results You Can Expect
Pituitary tumors have excellent outcomes with 5-year survival rates of 97%. Surgical cure rates for microadenomas reach 80-90%. For macroadenomas, surgery effectively relieves pressure, improves vision, and controls hormone levels. Approximately 35% of patients with pre-operative pituitary dysfunction recover function after surgery. Without radiation therapy, regrowth rates range from 6-46%, while with radiation therapy, regrowth occurs in 0-36% of cases. Most patients achieve excellent long-term outcomes with appropriate treatment.
Craniopharyngiomas treated with complete surgical resection have recurrence-free survival of 79% at 10-20 years. Subtotal resection followed by radiotherapy achieves 67% recurrence-free survival at 10-20 years. Overall good outcome rates reach 60.3% with mean follow-up of 10 years. Recurrence is the most common complication, with 20-30% of patients experiencing recurrence within five years after initial treatment. Reoperation can be curative, especially for solid tumor recurrences.
Why Choose The Brain and Spine Centre
Led by Dr. Muhammad Aqeel Natt, specialist neurosurgeon with extensive expertise in pituitary tumor surgery, craniopharyngioma management, and complex skull base surgery. Access to advanced imaging including high-field MRI for precise diagnosis and surgical planning. Minimally invasive transsphenoidal surgical techniques for optimal outcomes and faster recovery. Multidisciplinary team approach coordinating neurosurgery, endocrinology, neuro-oncology, radiation oncology, and ophthalmology. Convenient location at Farooq Hospital, West Wood Branch, Lahore with state-of-the-art operating and endocrine care capabilities.
Cost of Glioma Treatment
Costs vary with tumor type, size, surgical approach, need for radiation therapy, hormone replacement requirements, and duration of follow-up care. Personalized estimates provided after consultation and imaging evaluation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can I know Dr. Muhammad Aqeel Natt’s credentials?
What types of brain tumours do you treat?
Is the surgery safe?
Do I need long-term follow-up after surgery?
Are you having health problems? Contact us today!
Address Business
Contact With Us
Call Us 24/7: 0318 4065914
Working Time
Sunday: 8.30am - 19.30pm

