At The Brain and Spine Centre, we specialize in the diagnosis and surgical treatment of neurological and spinal disorders. Dr. Muhammad Aqeel Natt, a leading neurosurgeon in Lahore, provides advanced, safe, and compassionate care for patients.

Posterior Fossa Tumors
Posterior fossa tumors require prompt, expert diagnosis and specialized surgical treatment to relieve symptoms and preserve neurological function. At The Brain and Spine Centre, Dr. Muhammad Aqeel Natt provides advanced care for posterior fossa tumors at Farooq Hospital, West Wood Branch, Lahore, combining cutting-edge neurosurgical expertise with compassionate support.
Our goal is simple: remove tumor safely, restore neurological function, and guide recovery for the best possible quality of life.
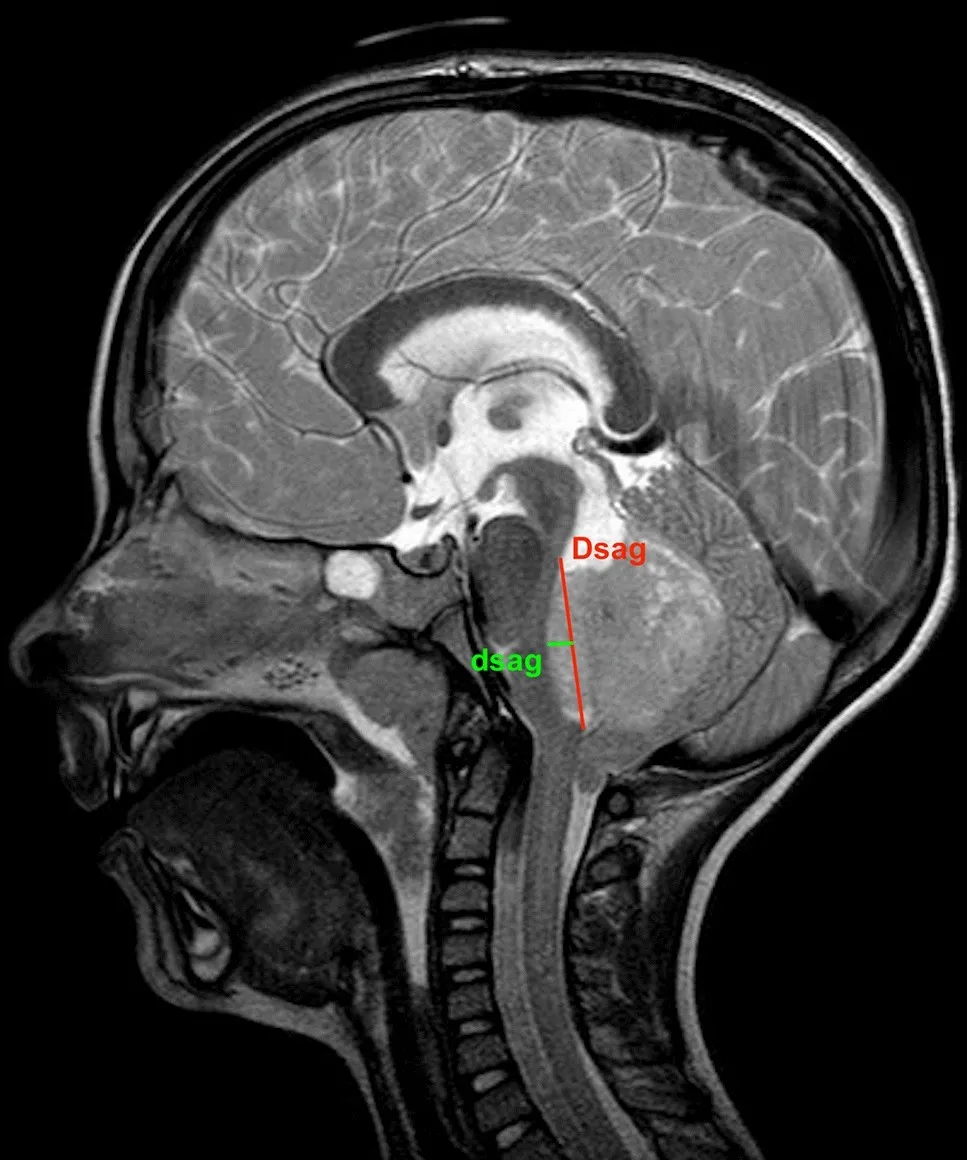
What Are Posterior Fossa Tumors?
Posterior fossa tumors are abnormal growths located in the back portion of the skull that contains the cerebellum and brainstem. The posterior fossa is a critical area responsible for motor movements, balance, coordination, and vital functions including heart rate, breathing, and consciousness. These tumors can occur in patients of all ages, though certain types are more common in children while others predominantly affect adults.
Common types of posterior fossa tumors include:
Medulloblastomas, ependymomas, and pilocytic astrocytomas (more common in children), meningiomas, acoustic neuromas (vestibular schwannomas), hemangioblastomas, and metastases (more common in adults), and diffuse midline gliomas affecting the brainstem.
Symptoms of Posterior Fossa Tumors
Symptoms occur when the tumor presses on or damages local brain structures and cranial nerves.
Common posterior fossa tumor symptoms include:
Headache, the most common symptom, particularly worse in the morning, nausea and vomiting due to increased intracranial pressure, drowsiness or altered consciousness, imbalance and uncoordinated walk (ataxia), gait abnormalities and difficulty walking, vision problems including blurred vision, double vision, or vision loss, hearing loss or tinnitus (ringing in ears), facial muscle weakness or numbness, difficulty swallowing or speaking, dizziness, and dilated pupils.
In infants and very young children, obstructive hydrocephalus results in macrocephaly with bulging fontanelle. Brainstem tumors commonly present with cranial nerve palsies, pyramidal tract signs (weakness, hyperreflexia), and cerebellar signs (incoordination, tremor).
Diagnosis
Diagnosis begins with neurological examination testing balance, coordination, vision, cranial nerve function, and motor strength.
Imaging studies are essential:
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is the imaging modality of choice for evaluating posterior fossa tumors. MRI provides superior soft tissue contrast and helps identify tumor type, location, and extent. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) measurements offer additional insights into tumor cellularity and malignancy potential. Advanced MRI sequences help differentiate between tumor types such as medulloblastomas (which show restricted diffusion due to high cellularity) and pilocytic astrocytomas (which typically lack diffusion restriction).
Computerized Tomography (CT) scan may be used in emergency settings to rapidly assess for hydrocephalus, hemorrhage, or when MRI is unavailable.
Additional testing may include spinal MRI to evaluate for metastatic disease, particularly in medulloblastomas where 10-45% may have spinal spread at initial presentation.
Treatment Options
Surgery: Surgical removal is the preferred treatment for most posterior fossa tumors when feasible. The goal is maximal safe tumor resection while preserving neurological function. The most common surgical approaches include midline suboccipital, paramedian suboccipital, and retromastoid (retrosigmoid) approaches. Positioning may be prone, lateral, or sitting depending on tumor location and patient anatomy. Surgery typically takes several hours depending on tumor size, location, and complexity.
Management of hydrocephalus: Many patients with posterior fossa tumors present with obstructive hydrocephalus requiring urgent treatment. Options include tumor resection alone (which often resolves hydrocephalus), external ventricular drain (EVD) placement for temporary CSF diversion, endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV) to create alternative CSF pathway, or ventriculoperitoneal shunt (VPS) for permanent CSF diversion.
Radiation therapy: Radiation may be used after surgery for malignant tumors, incompletely resected tumors, or recurrent disease. Medulloblastomas typically receive craniospinal radiation plus tumor bed boost.
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is standard treatment for medulloblastomas and may be used for other malignant posterior fossa tumors.
Rehabilitation: Comprehensive rehabilitation addresses motor, speech, cognitive, and behavioral deficits following surgery.
The Procedure
Our process safeguards safety, functional preservation, and optimal outcomes:
Consultation: Comprehensive neurological evaluation and imaging review to assess tumor type, location, symptoms, and surgical approach.
Imaging: Advanced MRI including DWI, conventional sequences, and spinal imaging when indicated to characterize tumor and assess for metastatic disease.
Surgery: Carefully planned suboccipital approach using microsurgical techniques and intraoperative monitoring to achieve maximal tumor resection while protecting brainstem, cerebellum, and cranial nerves.
Hydrocephalus management: EVD placement if needed for acute hydrocephalus, with definitive CSF diversion if hydrocephalus persists after tumor removal.
Recovery: Inpatient monitoring typically 8-10 days in the hospital, followed by rehabilitation and ongoing care.
Recovery & Aftercare
Recovery varies based on tumor type, extent of resection, and patient age. Most patients spend an average of 8 days in the hospital after posterior fossa tumor surgery. Approximately 75% of patients show improvement in symptoms after surgery.
Posterior fossa syndrome (cerebellar mutism) develops in approximately 25% of children undergoing posterior fossa surgery, particularly for midline tumors. Symptoms typically appear 24-48 hours after surgery and include mutism, emotional changes, motor deficits, and behavioral disturbances. Recovery from posterior fossa syndrome usually takes 6 months, though some children have residual deficits years after surgery. Early intensive rehabilitation including physical, occupational, and speech therapy is essential.
Rehabilitation addresses motor deficits, balance difficulties, speech and language problems, cognitive impairments, and behavioral symptoms. Multidisciplinary rehabilitation programs show clear efficacy in improving attention, metacognitive skills, executive functions, and quality of life.
Common postoperative complications include hydrocephalus requiring permanent shunt (58.3%), CSF leak (58.3%), wound infection (12.5%), perioperative edema (16.6%), tumor bed hemorrhage (6.2%), and pneumonia (5.3%). Most complications are not permanent and can be reversed with additional treatment.
Long-term follow-up with neurological assessments and imaging monitors for tumor recurrence and manages late effects of treatment.
Results You Can Expect
Survival outcomes vary by tumor type and grade. For benign pilocytic astrocytomas, 25-year survival exceeds 94%. For ependymomas, 5-year survival ranges from 67-80%. For medulloblastomas, observed 5-year survival is approximately 55-60%, with 20-year survival of 51% and 30-year survival of 44%.
Functional outcomes: Approximately 75-90% of patients achieve satisfactory surgical outcomes with symptom improvement. Good to moderate recovery is reported in 76% of patients at one year postoperatively. About 31% of patients have an uneventful postoperative course.
Quality of life: Most children surviving posterior fossa tumors show gradual improvement in quality of life during the first year after surgery. Children without cerebellar mutism syndrome have significantly better long-term quality of life compared to those with the syndrome. Factors associated with lower quality of life include cerebellar mutism syndrome, chemotherapy, VP shunt placement, and older age at surgery.
Tumor control: Successful tumor resection prevents further growth and relieves compression of vital brainstem structures. Recurrence rates depend on tumor type and completeness of resection.
Why Choose The Brain and Spine Centre
Led by Dr. Muhammad Aqeel Natt, specialist neurosurgeon with extensive expertise in complex posterior fossa surgery and microsurgical techniques. Access to advanced imaging including high-field MRI with DWI for precise diagnosis and surgical planning. State-of-the-art operating capabilities with intraoperative monitoring for maximal tumor resection and functional preservation. Multidisciplinary team approach coordinating neurosurgery, neuro-oncology, radiation oncology, and comprehensive rehabilitation services. Convenient location at Farooq Hospital, West Wood Branch, Lahore with intensive care and rehabilitation capabilities.
Cost of Posterior Fossa Tumor Treatment
Costs vary with tumor type, surgical complexity, need for hydrocephalus management, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, duration of hospitalization, and rehabilitation services. Personalized estimates provided after consultation and imaging evaluation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can I know Dr. Muhammad Aqeel Natt’s credentials?
What types of brain tumours do you treat?
Is the surgery safe?
Do I need long-term follow-up after surgery?
Are you having health problems? Contact us today!
Address Business
Contact With Us
Call Us 24/7: 0318 4065914
Working Time
Sunday: 8.30am - 19.30pm

